What is Network Segmentation?
Network segmentation divides a computer network into smaller segments or sub-networks to improve performance, security, and control. It involves creating multiple networks or sub-networks (segments) within a single physical network to isolate each network segment from the others. Network segmentation is a critical component of network architecture that divides a single physical network into multiple logical networks.
The administrative practice of Network segmentation involves breaking up massive networks into smaller sub-networks. It is considerably simpler to set up monitoring, identify network inefficiencies, and strengthen its security after segmenting the network.
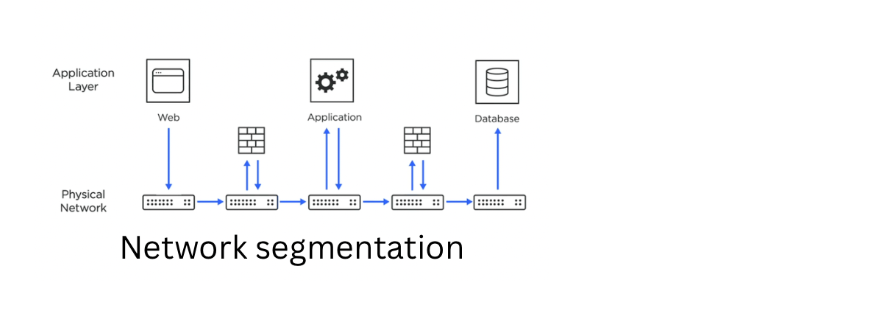
Network segmentation is essential for various reasons, including improving the performance of a network, increasing security, and controlling traffic flow. Breaking down an extensive network into smaller segments allows for more efficient bandwidth use, which can reduce latency, increase performance, and limit the risk of security threats.
Additionally, network segmentation can help control the flow of traffic and decrease the chances of network congestion.
Why do businesses need network segmentation?
IT infrastructure security is one of the essential assets for contemporary companies. Network segmentation is a valuable strategy for doing this and lowering cybersecurity costs. Plans for segmenting data based on a perimeter are being replaced by more contemporary ones that better meet the demands of the corporate world today.
Network segmentation helps establish team boundaries and enforces security regulations to stop data leaks. Moreover, it aids in distributing network traffic, improving performance uniformly.Companies like Fedstack, specializing in modernizing federal IT infrastructure, help organizations implement this network segmentation effectively.
Benefits of Network Segmentation:
Network segmentation can provide several benefits to businesses, including improved network performance, increased security, and more control over traffic flow.
The most significant advantages of segmentation are that it enables a corporation to increase sub-segment isolation, assure more challenging access control, introduce monitoring, optimize network performance, and achieve regulatory compliance status. It is a straightforward yet revolutionary advancement in network security.
Improved Performance:
Network segmentation can help improve the performance of a network by reducing the amount of traffic that needs to be routed. Dividing a single physical network into multiple logical networks allows for more efficient bandwidth use and can reduce latency, increase performance, and limit the risk of security threats. Additionally, network segmentation can help control the flow of traffic and decrease the chances of network congestion.
Increased Security:
Network segmentation can also increase the security of a network by isolating each segment from the others. Isolating each segment prevents malicious traffic from moving between segments and can help protect the network from attacks. Additionally, network segmentation can help prevent the spread of malware or malicious code, as each segment is isolated.
More Control Over Traffic Flow:
Network segmentation can also provide more control over the flow of traffic. Isolating each segment allows for more granular control over the traffic flow and can help prevent the spread of malicious traffic or code between segments. Additionally, network segmentation can help prevent congestion by preventing traffic from one segment from overwhelming another.
Implementing Network Segmentation:
When implementing network segmentation, it’s essential to consider the needs of the network and the types of traffic that will be running on it. Once the network requirements have been determined, it’s essential to identify the segments that need to be created and the appropriate type of segmentation that should be used.
The most common types of network segmentation include VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks), VXLANs (Virtual Extensible LANs), and subnets (IP subnetting). VLANs are used to segment traffic on a single physical network, while VXLANs are used to segment traffic across multiple physical networks. IP subnetting further divides a single VLAN or VXLAN into multiple subnets.
When implementing network segmentation, it’s essential to consider the security requirements of each segment, as well as the type of traffic that will be running on it. Additionally, when creating VLANs or VXLANs, it’s essential to consider the administrative overhead required to maintain the segmented network.
Segmenting the network can significantly lessen the impact of assaults. A network is segmented when split into several smaller networks, each functioning as a separate network called a subnet. Traffic movement across subnets can be managed by permitting or prohibiting it following several criteria or, if required, banning it altogether.
Conclusion:
Network segmentation is a critical component of network architecture and can provide various benefits to businesses, including improved performance, increased security, and more control over traffic flow.
When implementing network segmentation, it’s essential to consider the needs of the network, the types of traffic that will be running on it, and the security requirements of each segment. By utilizing network segmentation, businesses can improve the performance and security of their network, as well as control traffic flow.
Network segmentation makes sense since it may be used to implement tighter restrictions for crucial assets. Barriers can be built to prevent the implementation of Zero Trust across the network architecture by configuring user access rights for each subnetwork.